What is HFC transmission equipment? How does it work?
As the global demand for broadband access continues to rise, network transmission technology continues to evolve. Among them, HFC (Hybrid Fiber-Coaxial) hybrid fiber-coaxial network is still widely used in cable TV, broadband Internet access, voice communication and other fields due to its high cost-effectiveness and good scalability. As the core of the HFC network, HFC transmission equipment is responsible for efficient signal transmission and management from the head end to the user terminal.
1. What is HFC transmission equipment?
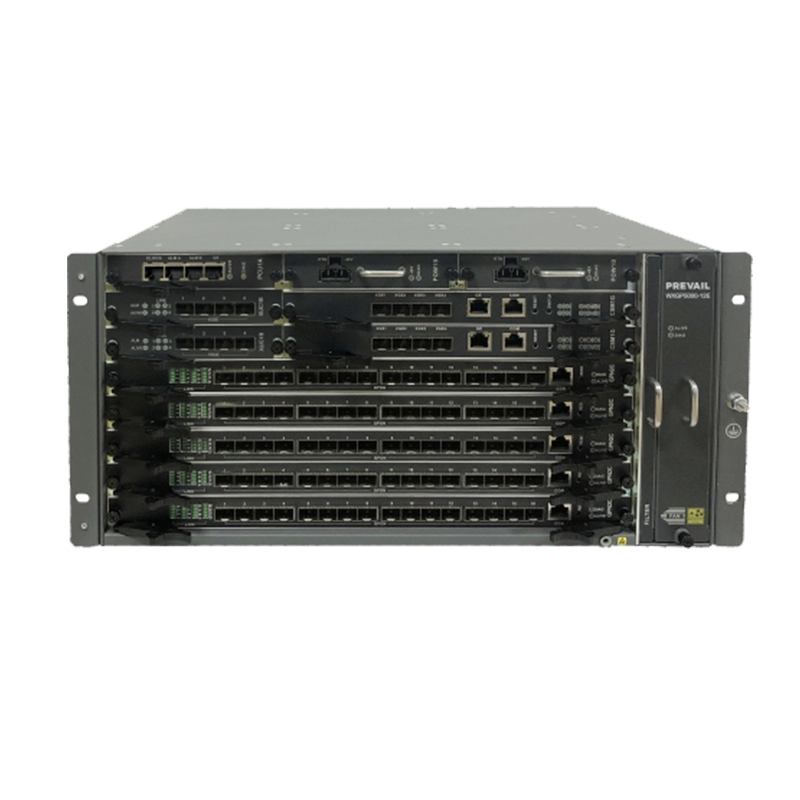
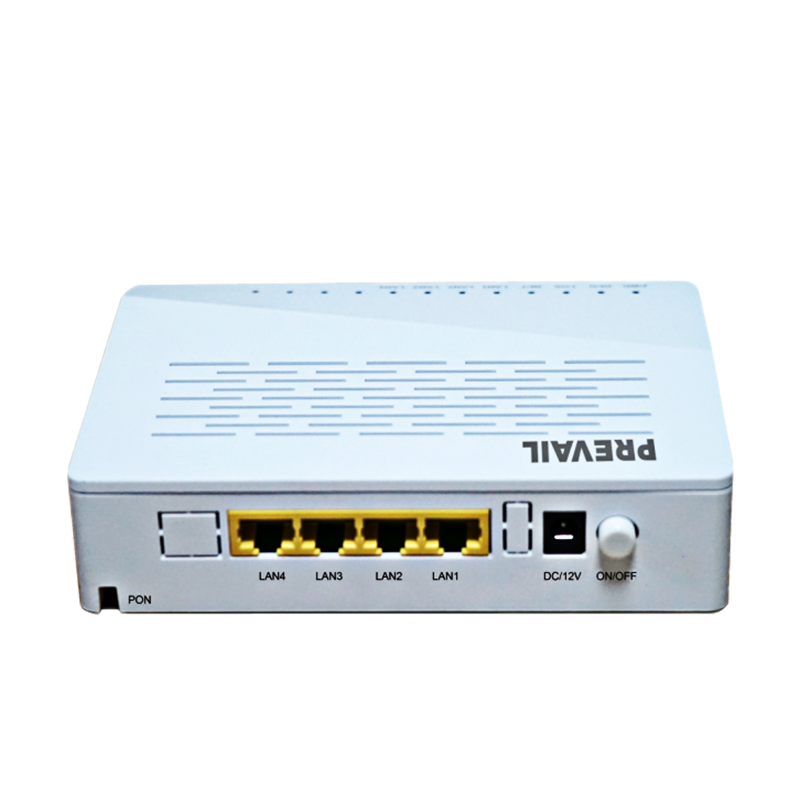
HFC transmission equipment (Hybrid Fiber-Coaxial Transmission Equipment) refers to a collection of various equipment used in hybrid fiber-coaxial networks to complete signal modulation, transmission, amplification, distribution and management. It supports the three-network convergence transmission of TV signals, Internet data and voice services, and is widely used in the access layer networks of cable TV operators and broadband service providers.
HFC networks use optical fiber for backbone transmission and coaxial cable for "last mile" access, combining the advantages of both to achieve a good balance between cost and bandwidth.

2. Basic architecture of HFC network
HFC network usually consists of the following four parts:
Headend system: the center for signal source (TV content, data, voice) aggregation and modulation;
Fiber backbone transmission: using optical cable to transmit signals from the headend to the optical node;
Optical node: converting optical signals into radio frequency (RF) signals;
Coaxial access: sending RF signals to user terminals (set-top boxes, modems, etc.);
HFC transmission equipment has a corresponding core role in each link.
3. Main components of HFC transmission equipment
1. Optical transmitter
Convert the modulated RF signal into an optical signal;
Mostly used for uplink transmission of TV signals.
2. Optical receiver
Receive the optical signal and convert it into an RF signal, which is sent to the coaxial network;
Installed at the optical node or remote site.
3. RF Amplifier
Amplifies RF signals and compensates for attenuation caused by long-distance transmission;
It is divided into trunk amplifier, branch amplifier and user amplifier.
4. Optical Node
Core conversion point: optical → RF;
Can support two-way transmission (uplink/downlink).
5. CMTS (Cable Modem Termination System)
Located at the head end, communicates with the Cable Modem at the user end;
Realizes access management of broadband data (such as DOCSIS protocol).
6. Splitter and Taps
Used for multi-user signal distribution in coaxial networks;
Controls attenuation and level balance.
7. Cable Modem
User-end equipment, providing Internet access;
Works with CMTS to achieve data transmission.
4. Detailed explanation of the working principle of HFC transmission
The basic process of HFC transmission is as follows:
Signal acquisition and modulation
TV, data, and voice signals are modulated into RF signals at the head end.
Optical transmission
The RF signal is converted into an optical signal through an optical transmitter and transmitted to each optical node through an optical cable.
Optical node signal conversion
The optical node converts the optical signal into an RF signal again and injects it into the coaxial network.
RF amplification and distribution
After amplification by the amplifier, the signal is distributed to each branch and finally transmitted to the user's home.
User terminal reception and analysis
The user receives TV signals through a set-top box or accesses the Internet through a Cable Modem.
Throughout the process, two-way transmission of signals is also achieved:
Downlink: head end → user (TV, data)
Uplink: user request → CMTS (such as network request)
5. Advantages of HFC network
Advantages Description
Low deployment cost The coaxial network has a wide foundation, and the upgrade cost is much lower than FTTH
Supports the integration of three networks Can transmit TV, data, and voice at the same time
High bandwidth scalability With the DOCSIS protocol, it can support speeds above 1000M
Mature and stable After years of operation verification, rich maintenance experience